Min. 6 students per class
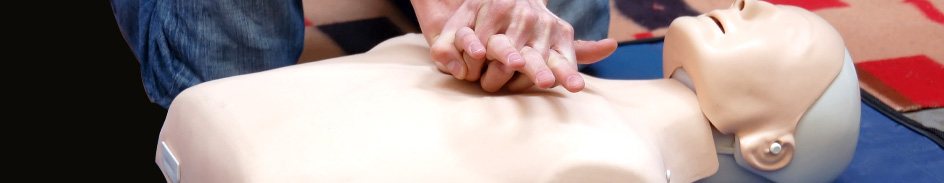
CPR and FIRST AID
TRAINING
Serving Central and Northern California since 1989





Complies with OSHA Requirements
California State Emergency Services Authority
Journal of the American Medical Association
California State Emergency Services Authority
Journal of the American Medical Association
CLASSES AVAILABLE 24 HOURS A DAY

California CPR and FIRST AID Classes
1-888-722-SAFE
We will come to you and furnish all equipment and supplies.

Give us a call
CPR911.ORG
Welcome to the Cal Safety CPR and First Aid Training website.We have been teaching California safety classes for over 20 years and we are all ways updating our material to keep up with all changes in basic emergency care.Our CPR and First Aid classes are taught by experienced Emergency Professionals in a fun and relaxed atmothphere.
STAFF@CPR911.ORG

California Safety Classes 24/7
1-888-722-SAFE
1-888-722-SAFE
Heat and Cold Treatment

Heat Exhaustion and Heat Stroke Treatment
Home care is appropriate for mild forms of heat exhaustion. Heat stroke is a medical emergency, and an ambulance should be called immediately.
* For mild cases of heat exhaustion
* Rest in a cool, shaded area.
* Give cool fluids such as water or sports drinks (that will replace the salt that has been lost). Salty snacks are appropriate as tolerated.
* Loosen or remove clothing.
* Apply cool water to skin.
* Do not use an alcohol rub.
* Do not give any beverages containing alcohol or caffeine.
*
* Heat stroke (do not attempt to treat a case of heat stroke at home, but you can help while waiting for medical assistance to arrive.)
* Call 911 immediately
* Move the person to a cooler environment, or place him or her in a cool bath of water (as long as he or she is conscious and can be attended continuously).
* Alternatively, moisten the skin with lukewarm water and use a fan to blow cool air across the skin.
* Give cool beverages by mouth only if the person has a normal mental state and can tolerate it.
Home care is appropriate for mild forms of heat exhaustion. Heat stroke is a medical emergency, and an ambulance should be called immediately.
* For mild cases of heat exhaustion
* Rest in a cool, shaded area.
* Give cool fluids such as water or sports drinks (that will replace the salt that has been lost). Salty snacks are appropriate as tolerated.
* Loosen or remove clothing.
* Apply cool water to skin.
* Do not use an alcohol rub.
* Do not give any beverages containing alcohol or caffeine.
*
* Heat stroke (do not attempt to treat a case of heat stroke at home, but you can help while waiting for medical assistance to arrive.)
* Call 911 immediately
* Move the person to a cooler environment, or place him or her in a cool bath of water (as long as he or she is conscious and can be attended continuously).
* Alternatively, moisten the skin with lukewarm water and use a fan to blow cool air across the skin.
* Give cool beverages by mouth only if the person has a normal mental state and can tolerate it.
Cold Treatment
* The first priority is to perform a careful check for breathing and a pulse and initiate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) as necessary
.
* If the person is unconscious, having severe breathing difficulty, or is pulseless, call 911 for an ambulance.
* Because the victimís heartbeat may be very weak and slow, the pulse check should ideally be continued for at least 1 minute before beginning CPR. Rough handling of these victims may cause deadly heart rhythms.
* The second priority is rewarming.
* Remove all wet clothes and move the person inside.
* The victim should be given warm fluids if he or she is able to drink, but do not give the person caffeine or alcohol.
* Cover the personís body with blankets and aluminum-coated foils, and place the victim in a sleeping bag. Avoid actively heating the victim with outside sources of heat such as radiators or hot water baths. This may only decrease the amount of shivering and slow the rate of core temperature increase.
* Strenuous muscle exertion should be avoided.
* Some cold exposure, such as cold hands and feet, may be treated with home care techniques.
* The first priority is to perform a careful check for breathing and a pulse and initiate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) as necessary
.
* If the person is unconscious, having severe breathing difficulty, or is pulseless, call 911 for an ambulance.
* Because the victimís heartbeat may be very weak and slow, the pulse check should ideally be continued for at least 1 minute before beginning CPR. Rough handling of these victims may cause deadly heart rhythms.
* The second priority is rewarming.
* Remove all wet clothes and move the person inside.
* The victim should be given warm fluids if he or she is able to drink, but do not give the person caffeine or alcohol.
* Cover the personís body with blankets and aluminum-coated foils, and place the victim in a sleeping bag. Avoid actively heating the victim with outside sources of heat such as radiators or hot water baths. This may only decrease the amount of shivering and slow the rate of core temperature increase.
* Strenuous muscle exertion should be avoided.
* Some cold exposure, such as cold hands and feet, may be treated with home care techniques.